Cloud Computing
- Benefits & Risks
- Deployment Models
- Service Models
- Characteristics
- Cloud Security
- FAQs
- Tools
- References
Benefits & Risks
- Benefits
- Cost effective
- No software installation required
- High efficiency, reliability & flexibility
- On-demand self-service
- Online development & deployment
- Risks
- Security & Privacy - any security breach may compromise sensitive customer data
- Lock-In - difficult for clients to switch from one Cloud Service Provider (CSP) to another
- Isolation Failure - failure of isolation mechanism that separates storage, memory, and routing between the different tenants.
Deployment Models
- Public Cloud
- The public cloud allows systems and services to be easily accessible to the general public. Public cloud may be less secure because of its openness.
- Private Cloud
- The private cloud allows systems and services to be accessible within an organization. It is more secured because of its private nature.
- Community Cloud
- The community cloud allows systems and services to be accessible by a group of organizations.
- Hybrid Cloud
- The hybrid cloud is a mixture of public and private cloud, in which the critical activities are performed using private cloud while the non-critical activities are performed using public cloud.
Service Models
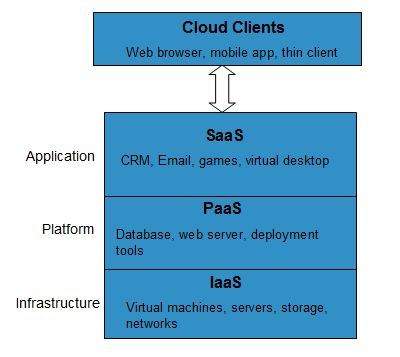
Infrastructure-as–a-Service (IaaS)
- IaaS is the most basic level of service. Each of the service models inherit the security and management mechanism from the underlying model, as shown in the following diagram
- E.g., physical machines, virtual machines, virtual storage, etc.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- PaaS provides the runtime environment for applications, development and deployment tools, etc.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
- SaaS model allows to use software applications as a service to end-users.
- E.g., Gmail, Google Docs
- Modes of SaaS
- Software as a Service provides cloud application platform on which user can create application with the tools provided.
- The modes of software as a service are defined as:
- Simple multi-tenancy: in this each user has its own resources that are different from other users. It is an inefficient mode where the user has to put more time and money to add more infrastructure if the demand rises in less time to deliver.
- Fine grain multi-tenancy: in this the functionality remains the same that the resources can be shared to many. But it is more efficient as the resources are shared not the data and permission within an application.
Anything-as-a-Service (XaaS)
Anything-as-a-Service (XaaS) is yet another service model, which includes Network-as-a-Service, Business-as-a-Service, Identity-as-a-Service, Database-as-a-Service or Strategy-as-a-Service.
Characteristics
- On Demand Self Service
- Cloud Computing allows the users to use web services and resources on demand. One can logon to a website at any time and use them.
- Broad Network Access
- Since cloud computing is completely web based, it can be accessed from anywhere and at any time.
- Resource Pooling
- Cloud computing allows multiple tenants to share a pool of resources. One can share single physical instance of hardware, database and basic infrastructure.
- Rapid Elasticity
- It is very easy to scale the resources vertically or horizontally at any time. Scaling of resources means the ability of resources to deal with increasing or decreasing demand.
- The resources being used by customers at any given point of time are automatically monitored.
- Measured Service
- In this service cloud provider controls and monitors all the aspects of cloud service. Resource optimization, billing, and capacity planning etc. depend on it.
Cloud Security
- Open only the ports absolutely necessary to support a server’s service and nothing more
- Even if you are not doing load balancing, use a reverse proxy. A reverse proxy is a web server such as Apache that proxies traffic from a client to a server.
Hardening
- Hardening an operating system is the act of minimizing attack vectors into a server. It involves the following activities:
- Removing unnecessary services.
- Removing unnecessary accounts.
- Running all services as a role account (not root) when possible.
- Running all services in a restricted jail when possible.
- Verifying proper permissions for necessary system services.
- The best way to harden your Linux system is to use a proven hardening tool such as Bastille.
- Avoid using “kitchen sink” Linux distributions. Each machine image should be a hardened operating system and have only the tools absolutely necessary to serve its function.
Network security system
| Perimeter Network Security System | Cloud Network Security System |
|---|---|
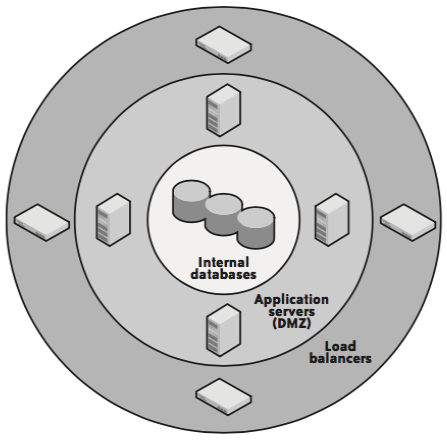 |
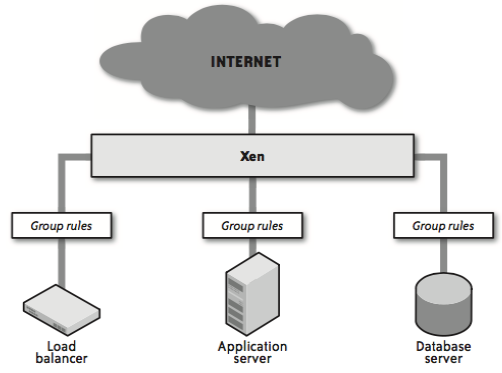 |
Load balancer -> Web server (reverse proxy) -> App server -> DB server- Use Intrusion detection software to detect Trojans in a server
- Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
- NIDS like Snort monitors local traffic for anything that looks irregular. E.g., port scans, DoS attacks, known vulnerability exploit attempts.
- Network intrusion detection exists to alert you of attacks before they happen and, in some cases, foil attacks as they happen.
- Port Scans and the Amazon Cloud
- When an attacker is looking for vulnerabilities against a particular target, one of the first things they do is execute a port scan against a known server and then examine servers with nearby IP addresses. This approach does not provide terribly useful data when executed against the cloud for a number of reasons:
- Nodes with proximate IP addresses are almost always unrelated. As a result, you cannot learn anything about the network architecture of a particular organization by executing a port scan.
- Amazon security groups deny all incoming traffic by default, and requests for ports that have not been opened simply do not respond. As a result, very few ports for any particular server will actually be open. Furthermore, scanning across all ports is a very slow process because each closed port times out instead of actively denying the traffic.
- Amazon has its own intrusion detection systems in place and does not allow its customers to execute port scans against their own servers. As a result, an active port scan is likely to be blocked before any real information can be gathered.
FAQs
- Difference between scalability and elasticity?
- Scalability is a characteristic of cloud computing through which increasing workload can be handled by increasing in proportion the amount of resource capacity. It allows the architecture to provide on demand resources if the requirement is being raised by the traffic.
- Whereas, elasticity is being one of the characteristic provide the concept of commissioning and decommissioning of large amount of resource capacity dynamically. It is measured by the speed by which the resources are coming on demand and the usage of the resources. Elasticity is reversible scability
- Cloudbursting
- A hybrid approach where many compute resources are kept private internally but when additional demand is needed, a public cloud is called upon to provide those temporary resources. This is called “Cloudbursting”
Tools
- Simian Army
- Chaos monkey - Self-healing system
References
- Books
- Cloud Application Architecture