Micro Frontend
- Web architecture types
- Micro frontends
- Isomorphic apps (SSR)
- PWA apps
- Web assembly
Micro FrontEnds
Micro Frontends are the technical representation of a business sub-domain, they allow independent implementations with same or different technology choices, finally they avoid sharing logic with other sub-domains and they are owned by a single team.
Advantages of Micro Frontends
- Ease of innovation
- Easy to manage
- Easy to upgrade to new component or technology
- Ease of deployment due to lack of inter-dependency
- Quick time to market
- Technology independence across frontends (but don’t do this)
- Each team has clear ownership
- Promotes Domain-Driven Design
Challenges in Micro Frontends
- first call takes a long time
-
difficult to be indexed by search engines, crawlers, etc.
- Share nothing across front ends e.g., CSS stylesheets
- Diamond anti-pattern
- Webcomponents.org
- Polymer-lit
- Stencil js
- Skate js (Netlify)
- Module loader - SystemJS
- Open Table
Design
Domain Modeling (DDD)
- Domains
- Sub-domains
- Core subdomain e.g., core business function like video streaming for Netflix
- Generic subdomain e.g., payment processing
- Supportive subdomain e.g., recommendation engine
- A team can own more than one subdomain
Design Considerations
4 things to consider in µFE architecture
1.Definition
- Use APIs First Design Principle
- APIs are the first user interface of your app
- APIs come first, then the implementation
2.Composition
- Client-side composition
- Edge-side composition
- Server-side composition
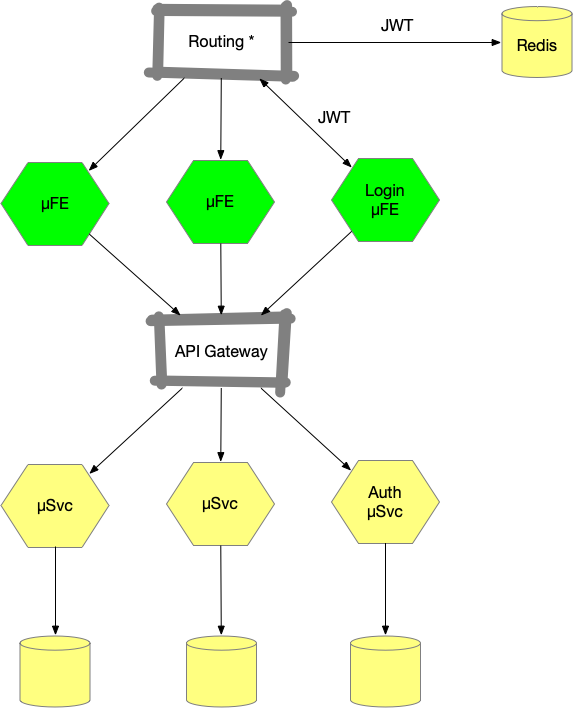
3.Routing
- Router is responsible for intercepting and validate JWTs before redirecting to a µFE page
4.Communication
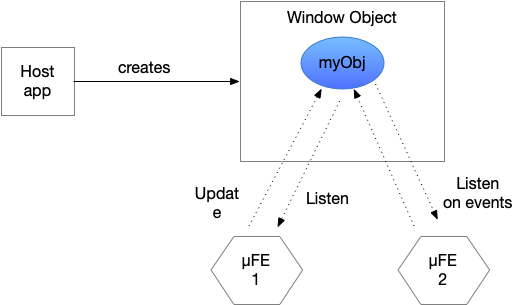
- e.g., window object or redux
- Window object is the centralized place where all the components in the page can access the data from. Kind of follows the Redux data flow pattern.
- Having a global object/variable in window object is against the µFE encapsulation?
Implementation
There are 3 things essential for any micro frontend application or framework.
- Load component scripts onto the page e.g., ScriptJS, SystemJS (module/component loader)
- Single SPA is layered on SystemJS
- Instantiate the components and place them in the DOM. e.g., SingleSPA
- Communication of data between the components
- SingleSPA leaves it up to you
Types of Implementation
- iFrames - used by Spotify
- Shell as proxy
- Common logic like auth can be shared in shell
- Web Components - Polymer
- Bootstrap
- Open Components - used by OpenTable
- Interface Framework - Zalando uses mosaic9, tailor.js
-
Edge Side Include (ESI) - used by IKEA
- Reverse proxy
- Auth logic must be duplicated in multiple places since Nginx can’t have business logic
- Using API gateway
- e.g., Ambassador
- Micro frontend ownership: a team must do all the below: develop, test, build, deploy, document, live-support
Open Questions
- how authentication works? how session management is handled?
- how communication between µFEs work?
- how multiple µFEs are integrated to form an app? build time or runtime?